Start with SHiNeMaS
User Reference Guide
File formats¶
The submission files in SHiNeMaS are « tabulated » files and must fit with the following rules :
Text file
Column separator : tabulation
Text delimiter : “
For example, a file open with a simple text editor, that will be submitted into SHiNeMaS must look like this :
"project" "location" "id_seed_lot" "etiquette" "event_year" "split" "quantity"
"PPB" "FLM" "Rouge-du-Roc_JFB_2004_0001" 2004 1 250
"PPB" "FLM" "Clomone_JFB_2004_0001" 2004 1 122
Each file type is described by mandatory fields (headers). It is possible to add additional columns regarding the method file (section Methods file ). With this feature a user can customize variables definition.
Methods file¶
The method file contains the description of measures and the methods used to make these measures. Four fields described this file :
variable : the name of the measured variable
type : the type of the variable (described in this section)
method_name : the name of the method used to measure this variable.
correlation_group : correlation groups used for this variable. Correlation groups usage is described in this section.
Events types¶
Cross-breeding¶
A cross-breeding event occur between different varieties, as shown on the figure below. A cross-breeding creates a new variety.
Cross breeding event¶
File headers :
The breeding file describes the information necessary to create a cross-breeding event in the database. The fields needed to create a breeding are the following :
project: Project in which the event has occurred
sown_year: Parents seeds lots’ sown year.
harvested_year: Harvest year of the seed lot descended from the cross-breeding
quantity_harvested: Quantity harvested after the cross-breeding. It is the initial quantity of the harvested seeds lot.
cross_year: Year of the cross-breeding
cross_germplasm: Name of the new created variety
number_crosses: Number of cross-breeding done
kernel_number_F1: Number of seeds obtained from the cross-breeding and used for the F1
male_seed_lot: ID of the seeds lot used as a male
male_etiquette: Label used for the male seed lot
male_split: Indicates if the entire seed lot was used at cross-breeding: 0 for all and 1 otherwise
male_quantity: Quantity of seeds from the seed lot used
male_block: Block in which the seed lot has been sown
male_X: X coordinate of the male seed lot
male_Y: Y coordinate of the male seed lot
female_seed_lot: Identifier of the seed lot used as female
female_etiquette: Label used for the female seed lot
female_split: Indicates if the entire female seed lot was used for the cross-breeding: 0 for all and 1 otherwise
female_quantity: Quantity of the female seed lot used
female_block: Block in which the female seed lot has been sown
female_X: X coordinate of the female seed lot
female_Y: Y coordinate of the female seed lot
Diffusion¶
This file is used to create diffusion events. A diffusion makes possible to send a seeds lot, entirely or partly, from a place A to a place B, as represented on Figure 11.
File headers:
The diffusion file describes the information needed to create a diffusion event in the database. The fields required to create a diffusion are:
project: Project in which the diffusion takes place
location: Place where the seed lot is diffused
id_seed_lot: Identifier of the “parent” sent seed lot
etiquette: Label used for the parent seed lot
event_year: Year of the diffusion
split: Indicates if the entire “parent” seed lot has been diffused: 0 for all and 1 otherwise
quantity: Quantity of seed lot released (“child” seed lot)
Mixture¶
This file is used to create mixture events as shown in Mixture event. A mixture consists in using at least two seeds lots and grouping them into a single seeds lot. There is no limit on the number of seed lots that can be mixed. However, all seed lots must come from the same place. A mixture leads to the creation of a new variety.
Mixture event¶
File headers:
The mixture file describes the information needed to create a mixture event in the database. The mixture file has the particularity of describing a mixture event on several lines of the file. Each line describes a lot of seeds used in the mixture. The germplasm field, repeated on several lines, makes possible to group the seeds lots that are used in the same mixture. The fields needed to create a mixture are:
project: Project in which the mixture has been done
id_seed_lot: Identifier of the « parent » seeds lot mixed
etiquette: Label used for the « parent » seeds lot
split: Indicates if the entire seeds lot has been used for the mixture : 0 for all and 1 otherwise
quantity: Quantity of the « parent » seeds lot mixed
germplasm: Name of the created new variety
event_year: Year of the mixture
Reproduction¶
This file makes it possible to create reproduction events as described on Figure 15. A reproduction takes place on a given place, at a given position, defined by its block and its X and Y coordinates. A reproduction consists in sowing a seed lot at one or more plots and then harvesting the seed lot(s).
File headers:
This file makes it possible to create reproduction events. A reproduction takes place on a given place, at a given position, defined by its block and its X and Y coordinates:
project: Project in which the reproduction takes place
sown_year: Sowing year of the parent seed lot
harvested_year: Harvest year of seed lot “child”
id_seed_lot_sown: ID of the « parent » sown seed lot
intra_selection_name: Name of the selection
etiquette: Label used for the « parent » seed lot
split: Indicates if the entire « parent » seed lot has been sown : 0 for all, 1 otherwise
quantity_sown: Quantity of the « parent » seed lot used
quantity_harvested: quantity harvested for the « child » seed lot
block: location block of the reproduction
X: coordinate X
Y: coordinate Y
Selection¶
This file is used to create selection events. A selection event is always associated with a reproduction. A selection can be made by an actor of the network.
File headers: The selection file describes the information needed to create a selection event in the database. The fields required to create a selection are :
project: Project in which the selection takes place
sown_year: Sowing year of the « parent » seed lot
harvested_year: Harvest year of seed lot « child »
id_seed_lot_sown: Identifier of « parent » seed lots
etiquette: Label used for the « parent » seed lot
block: block where the reproduction take place
X: X coordinate
Y: Y coordinate
selection_person: Short name informing the person who made the selection
selection_quantity_ini: Quantity selected
selection_name: Name given to this selection
Note that the selection_name can be used only one time for a specific germplasm. To help you to respect this rules you can use the selection table.
Individual data¶
This file is used to enter individual data concerning reproductions or selections. Individual data is associated with numbered individuals.
File headers:
The individual data file describes the information needed to insert individual data into the database. The fields required to insert this data are as follows:
project: Project in which the selection takes place
sown_year: Sowing year of the « parent » seed lot
harvested_year: Harvest year of seed lot « child »
id_seed_lot_sown: Identifier of « parent » seed lots
intra_selection_name: Name of selection if applicable
sown_etiquette:Label used for the « parent » seed lot
id_seed_lot_harvested: Identifier of the « child » seed lot harvested
harvested_etiquette: Label used for the «child» seed lot
block: block where the reproduction take place
X: X coordinate
Y: Y coordinate
individuals: Number of the individual
Correlation groups¶
Correlation groups are used for individual data. Let’s consider a data series (at a same date for example) on numerated individuals. For the next series (at another date) the user collect data on the same number of individuals. But two scenarios can occur :
The numerated individuals are not the same (You lost the numeration between the two series of data). In that case the data of the first series and the second series can’t be correlated as it’s haven’t be done on the same individuals. Example : In figure A, on a single line, data in green, blue and orange aren’t correlated and belongs to 3 different groups B, C, and D
The numerated individuals are the same. In that case all data can belong to the same correlation group. Example : In figure A, the lines in yellow. The data belongs to the group A.
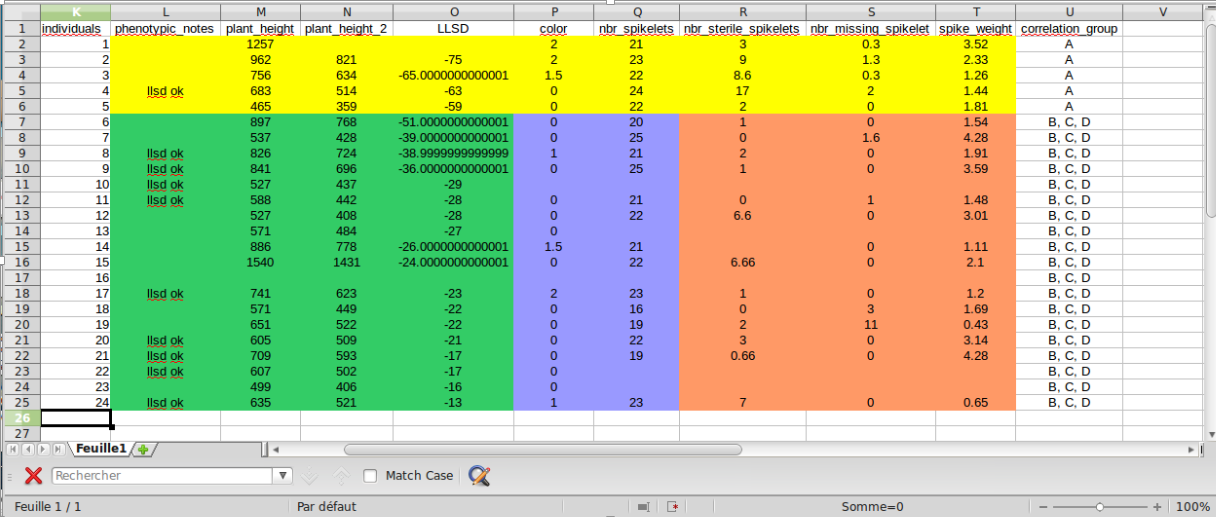
A : Reproduction file with correlation groups¶
In the method file you should report in the correlation_group column all the correlation groups in which a variable is implied (figure B). For example, the variable ‘plant_height’ is implied in the correlation groups A (yellow) and B (green).
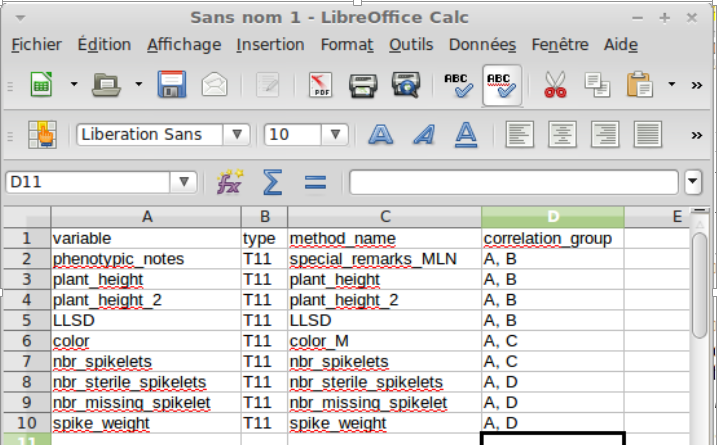
B : Method file with correlation groups¶
Particular cases¶
It is possible to measure a same variable with two different method. To do the variable must be tagged with a prefix in the data file and in the method file. The following syntax is used (Figure below) : prefix%variable_name
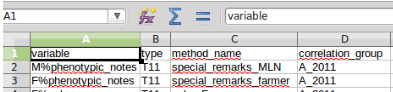
Variable using 2 differents methods¶